For each alignment produced by CLICK, a Z-score is computed to determine the significance of the alignment. In our case, the Z-scores are an estimate of the likelihood that the alignment is different an alignment made by chance. It is computed as
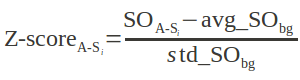
Where,
A is the query structure for which similar structures are sought in a database, whose members are the structures {Si}.
SOA-Si is the average structure overlap (computed over the representative atoms) on the superimposition of A and Si within cut-off distances of 1 Å, 2 Å, and 3 Å.
avg_SObg and std_ SObg are the average and standard deviation of structure overlap within 1 Å, 2 Å, and 3 Å of alignments
produced by aligning all members of a background database with one another. Background databases are chosen according to the submitted query.
For instance, for a query protein structure, the background database would be a non-redundant set of proteins structures consisting of 1601 chains.
Similarly, the DNA, RNA and DNA-protein complex databases consist of 107, 255 and 301 non-redundant structures respectively.
When the query structure is a fragmented chain of a structure that consists of N representative points, the same number of
The avg_SObg is then computed by an all-against-all alignment of these 30 selected extracts. For the comparisons of whole
molecules or for fragments containing more than 80 representative points, the background scores are computed by considering the all-against-all comparisons
of structures of 30 randomly chosen whole molecules.
For a significant match, Z-score should be above 2.5. The greater the Z-score the more significant is the match.